
Chronic pain has both a physical and an emotional component. People who suffer from anxiety are more likely to also suffer from chronic pain, and vice versa. As it turns out, chronic pain and anxiety work hand in hand. Chronic pain can make anxiety worse, and anxiety can also worsen chronic pain. It is important for chronic-pain patients to find strategies to cope with anxiety. The following are some simple ways to manage anxiety on a day-to-day basis:
- Take a time out. This simply means stepping away from the problem at hand by focusing attention on something else such as music, deep breathing, meditation, or any other activities that you find relaxing. Create a restful environment to help you accomplish this, trying to limit irritating noises, lights, or anything else that distracts you.
- Do your best. Appreciate what you can accomplish and commend yourself on the small tasks that you get through each day.
- Talk to a friend. Ask a friend or family member for help. This can alleviate some stress and allow you to feel less overwhelmed.
- Laugh. Humor has been shown to reduce anxiety.
- Keep a positive attitude. Try to focus on the positive things in your life to replace your negative thoughts.
- Eat well. Healthy eating makes for a better body and can help reduce stress and anxiety.
- Cut down your caffeine intake and other stimulants, as these substances are designed to increase the activity of your central nervous system.
Talk therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy with a mental health professional can also help you discover better ways to cope with your anxiety. You can even talk to your doctor about using medications in combination with these other strategies if your anxiety is very severe.
While chronic pain and anxiety are often difficult to deal with, these various coping strategies can put patients on the right track for overcoming chronic pain related anxiety.
Relaxation
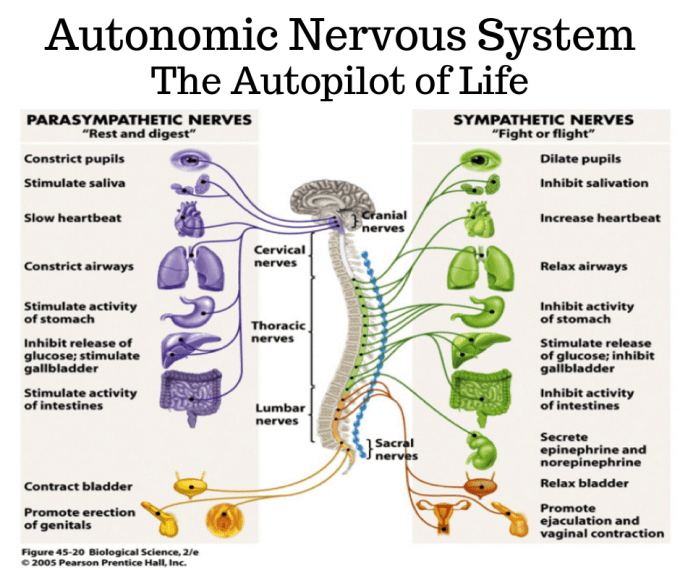
Relaxation is essential to achieving and maintaining better health, but it is not easy, especially in the face of life stressors that are out of your control. Many of the techniques listed above to help you cope with anxiety are relaxation exercises. Practicing relaxation techniques can have many benefits, decreasing the effects of stress on not only your mind, but also your body. When your body is stressed, your central nervous system fires up, sending out stress hormones that cause your heart to beat faster, your breathing to increase, your blood vessels to dilate and disrupts your digestive processes to prepare the body for action. Individuals with pain generally have dysregulated nervous systems, which can make it harder for you to bounce back to your baseline after painful events, and also significantly impacts your sleep.
Due to the impacts stress has on your sleep, one of the best times to start your relaxation program is before bed. You should start off with a ten minute relaxation program and you can gradually increase it as you improve your ability to bring your body to a relaxed state. Other examples of relaxation techniques include autogenic relaxation, using visual imagery and body awareness to reduce stress. An example of this is imagining yourself in a setting you find peaceful, like the beach and then focusing on controlling and relaxing your breathing. When you place yourself in a peaceful setting, try to incorporate as many senses as you can. If you’re imagining yourself at the beach, you can try to imagine the warmth of the sun on your skin, the sound of waves crashing, the smell of the salt air. Another common method of relaxation is progressive muscle relaxation, where you focus on slowly tensing and relaxing each muscle group also can help you become more aware and in control of your body. Relaxation techniques are skills, which means they take practice to learn and you’ll become better at it over time.
Relaxation techniques can help activate your parasympathetic nervous system, slowing your heartbeat, lowering your blood pressure, increasing blood flow to your muscles, improving your digestion, sleep, lowering your fatigue and anxiety, improving concentration and mood and can reduce your pain.
Check out the UF Center for Musculoskeletal Pain Research’s Recommended Relaxation Technique

